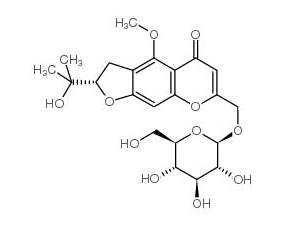
Cimifugin beta-D-glucopyranoside
CAS No. 80681-45-4
Cimifugin beta-D-glucopyranoside( —— )
Catalog No. M19131 CAS No. 80681-45-4
Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin can inhibit the proliferation of SMC(smooth muscle cell) stimulated by TNF-alpha, increase the proportion of G0/G1 phase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 110 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 200 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 338 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 498 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 710 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCimifugin beta-D-glucopyranoside
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPrim-O-glucosylcimifugin can inhibit the proliferation of SMC(smooth muscle cell) stimulated by TNF-alpha, increase the proportion of G0/G1 phase.
-
DescriptionPrim-O-glucosylcimifugin can inhibit the proliferation of SMC(smooth muscle cell) stimulated by TNF-alpha, increase the proportion of G0/G1 phase.
-
In VitroPrim-O-glucosylcimifugin (POG) is the highest content chromone and one of the major active constituents in Radix Saposhnikoviae (RS). Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 expression by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 signaling. The cytotoxicity of Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin is measured to LPS-activated Raw 264.7 macrophages. Raw 264.7 macrophages are treated with LPS (1 μg/mL) and increasing concentrations of Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin (15, 50, and 100 μg/mL) for 24 h and cell viability is evaluated by CCK-8 assay. Cell viability is not significantly affected after 24 h and exposure to 15-100 μg/mL Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin as compared with DMSO-treated cells (control). To investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin, whether Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin can affect NO synthesis is examined in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells. Macrophages are treated with LPS (1 μg/mL) and various concentrations of Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin (15, 50, and 100 μg/mL) for 24 h. No concentrations are measured in the culture supernatants by Griess reaction. The concentrations of NO in the culture supernatants are markedly increased in response to LPS exposure, and Prim-O-glucosylcimifugin significantly inhibits LPS-induced NO production in a concentration-dependent manner.
-
In VivoBronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) is collected at 7 h after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) administration and the cytokine levels in BALF are measured by ELISA. The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in BALF are increased dramatically compared with control group. However, pretreatment with Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin (2.5, 5 or 10 mg/kg) significantly down-regulates the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in a dose-dependent manner (P<0.05, P<0.01).
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorTNF-α
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number80681-45-4
-
Formula Weight468.45
-
Molecular FormulaC22H28O11
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 150 mg/mL; 320.20 mM
-
SMILESCC(C)([C@@H]1Cc2c(O1)cc1c(c2OC)c(=O)cc(o1)CO[C@H]1[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O1)CO)O)O)O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Zhao XL,et al. [Studies on effects of calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucoside on prim-O-glucosylcimifugin and cimifugin in vivo pharmacokinetics]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Palomid 529
Palomid 529 has been used in trials studying the treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration.
-
His-[D-2-ME-Trp]-Ala
His-[D-2-ME-Trp]-Ala is a fragment of the growth hormone hexarelin.
-
BAY1217389
BAY 1217389 is an effective and selective inhibitor of the monopolar spindle 1 (MPS1) kinase (IC50<10 nM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


